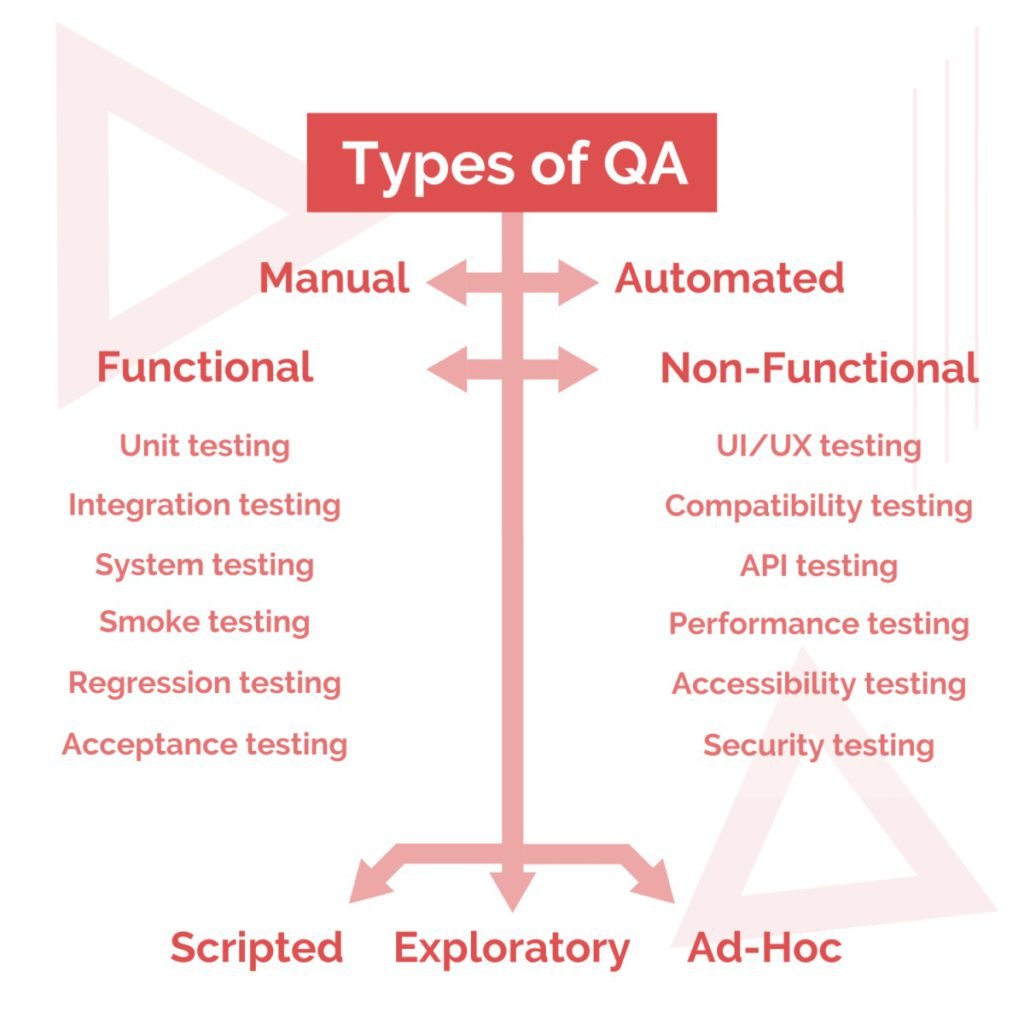
Let’s discuss automated and manual, scripted and exploratory, functional and non-functional software testing types and all their subtypes
Suppose that you’ve built an app that is expected to be a huge success. Why would you spend time and money making sure that you did everything correctly? You could just click through the app, make sure that everything works well, and push the app forward to the market, right? Not really…
Is Quality Control important only for software development? No, it’s not. If you look at different spheres closer, you’ll see that each business process highly relies on Quality Assurance and Control. When a chef works on a new menu, he tastes each new recipe to make sure that it is impeccable. When a crew prepares a plane for the takeoff, the airport maintenance team conducts a walk-around, while the pilots conduct pre-flight checks in the cockpit. When a surgeon prepares a patient for the operation, he assigns blood tests, CT scans, allergy tests, and other medical checks. Quality Assurance is the precondition of successful results in every field.
You might say that you understand the importance of software testing and QA services. And while the need for conducting effective software testing seems obvious for you, choosing the right instruments is not that easy. What are the stages of testing? What types of QA testing methodologies to use? Why and how? These questions look far more confusing.
In this article, I will look through different types of software testing, different software testing methodologies, where they should be used, and which benefits they bring.
Automated Testing vs Manual Testing
Let’s start with a broad typology. There are two broad types of testing: automated and manual. It is easy to differentiate between them because manual software testing technique is conducted manually by a QA specialist, while automated software testing is performed with the help of written code scripts — a code that tests code.
Like everything that can be automated, the automated software testing approach saves time and effort. Testing algorithms do everything for you and you finish your project quicker. Yet, applying automated testing is expensive. Meantime, opting for different types of manual testing is considerably cheaper than the automated one but usually takes longer and leaves more room for errors. Manual testing is more suitable when test cases need to be checked only once or twice, not repeatedly. Also, unlike automated tests, manual testing types identify nonfunctional issues that affect customer experience.
What type to focus on? For you as a business owner, the best decision is to consult an expert PM. They’ll tell you which type of Quality Assurance testing — manual or automated — suits your business needs better.
Scripted Testing vs Exploratory Testing vs Ad-hoc Testing
Scripted testing is performed with the help of test cases created in advance. Using test cases is a great idea for a tester who lacks experience and wants to follow the defined patterns and testing rules.
Another type of testing is exploratory. This type does not require test cases. During the exploratory testing sessions, a QA specialist investigates the system, randomly goes through each page, and estimates the overall feeling of the app. This testing type relies on cognitive thinking and can be conducted only manually. Yet, its main advantage is the human factor — it increases the possibility of errors and missing data.
Ad-hoc testing is the most informal and random among all the types of software quality assurance. Also called monkey testing, it aims to break the software system. It follows no documented procedures – instead, it prioritizes the result. The benefit of ad-hoc testing is that it can be conducted by anyone on the project, and the goal of it is to find errors and bugs that are not covered by test cases.
What’s the difference between the last two types? The former one is a mandatory step conducted while the app is being developed according to the described workflow, while the latter one is not mandatory, is conducted after the app is complete, and disregards the workflow. You can use this type of software testing as an additional way to ensure the high quality of the end product.
Functional Testing vs Non-Functional Testing
Functional testing focuses on functions, With this testing, you check whether all the functions and features of a software product are present and operate properly. Functional QA testing types include smoke testing, unit testing, integration testing, system testing, regression testing, and user acceptance testing.
Non-functional testing types check other, non-functional aspects of the software, such as performance, reliability, and security. Non-functional software testing practices include UI/UX testing, compatibility testing, API testing, performance and load testing, accessibility testing, and security testing.
What’s more important for your product: functional or non-functional testing? Both. Your client will not use an application that does not ensure data protection. Neither will they use an app that’s kind of buggy and does not give them customer satisfaction.
Unit Testing, Integration Testing, and System Testing
• Unit testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: Development team
When conducted: Before submitting a build for full-scale testing
The outcome: Finding and fixing major bugs instantly
Unit testing checks whether a unit performs as it should. It addresses not the entire software product but a single component of it, a single unit. Here, a unit is the smallest testable part of the software with a single output.
Unit testing is applied by developers before the app is sent to the Quality Assurance team. It is an automated type of testing that brings more confidence in code coverage. If proper unit tests are written after each major change in a code, bugs and defects can be promptly caught and solved. Also, unit testing increases the reusability of code. For unit tests to be conducted, the code has to be modular, and therefore, it becomes reusable.
• Integration testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: Testing or development team
When conducted: During development or testing
The outcome: Ensuring that components interact properly
Integration testing is the opposite of unit testing. Unit testing checks each component individually, while integration testing checks how they interact with each other. It is conducted after unit testing but prior to system testing.
Integration testing can be applied during the development stage by developers or during the Quality Assurance stage by testers. It can be both manual and automated. There are different approaches to integration testing: Bing Bang, Top Down, Bottom Up, Sandwich.
• System testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: Before the product is delivered
The outcome: Ensuring that the entire system functions properly
System testing checks if all the components perform well altogether as a system. The very name speaks for itself. System testing is conducted when the app is already ready to deploy. Performed by testers manually or automatically, this type of test helps them understand if the app can be delivered. If successful, the app is sent to a client for acceptance testing. If no, developers spend some time improving the application.
But how to differentiate between these three forms of testing? Let’s compare a software product to a tree: unit testing would be checking each particular leaf, integration testing would check each branch, and system testing would check the entire tree. That’s it.
• Smoke Testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: Between development and full-scale testing
The outcome: Optimizing QA process
Smoke testing is also known as build verification testing. It’s one of the most superficial types of Quality Assurance. Once the development team sends the project build to the software testing team, the latter checks if the build is stable and does not crash. They look through the most basic functionalities and decide whether the build is suitable for further, more detailed testing or it should be returned to the development team.
When should you go for smoke testing? When you want to reduce efforts and expenses spent on the QA process and identify problems timely. Similar to unit testing, if conducted after each change in the build, smoke testing can ensure the stability of the code.
• Regression Testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: When a new change is implemented
The outcome: Making sure that changes do not affect existing code
Under software regression testing, a QA specialist selects a certain portion of test cases and re-executes them fully or partially. This type of testing belongs to the functional group. It is conducted after a minor or major change in the code to check if this change does not affect the software somehow.
When conducting regression testing, one should not necessarily retest all test cases. It would be more rational to recheck test cases that concern the core software functionality and test cases of features that underwent the most changes. Also, those test cases with the most frequent defects and those most visible to the users deserve attention.
• Acceptance Testing
Type: Functional
Who conducts: PM, client
When conducted: When the product is being delivered
The outcome: Making sure that the software meets expectations
Acceptance testing is performed neither by a developer nor by a QA specialist. Acceptance testing is a functional testing type that is executed by a client and should involve all stakeholders.
Under acceptance testing, a client checks the software presented to them by the development team in order to find out if it fully meets project requirements. The outcome of this testing is the client’s decision to accept or not to accept the software product. As you might guess, before the client gets a product for a check, it should undergo many other types of testing. To earn client’s trust and satisfy them with the results, both developers and testers should take care of the quality via effective testing before a client sees a product.
• UI/UX Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: UI/UX designer
When conducted: When the product is designed
The outcome: Optimizing the app usability and user experience
UI/UX testing is quite different from any other type of testing, with its own procedures, methodologies, objectives, and concepts. UI/UX testing checks the efficiency of UI and UX design. It is one of the non-functional types of testing, which looks for the optimal way of interaction between a software product and the target audience.
UI/UX testing is an essential part of the Business Analysis process. It is conducted prior to the development and helps to greatly improve the project idea before implementing it, which would boost the outcome brought by a product, minimize the probability of logical mistakes, and increase the efficiency of development.
Check my recent article “The Value of User Testing: How to Find the Hidden Opportunity?”.
• Compatibility Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: During full-scale testing
The outcome: Making sure that the app works on any software and hardware
Compatibility testing is of crucial importance for user engagement and retention. The idea of compatibility testing, a non-functional testing type, is to make sure that a software product can function properly on any device, any OS, and any browser.
QA specialists run and test the product on different operating systems of different versions, different hardware, networks, and browsers. If a person launched the app on their device and it did not work properly, they would give your software product no second chance.
• API Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: Developers or testing team
When conducted: During development
The outcome: Making sure that the API of the app functions properly.
API testing is one of the non-functional types of testing, and it checks how the application interacts with API (application programming interface). Performed at the message layer, API testing can identify such errors as unused flags, performance issues, security issues, or reliability issues.
This type of testing determines if the API returns responses for different requests correctly and timely, if it reacts properly to failures or improper inputs, and if it responds securely to possible system data attacks.
• Performance Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: During full-scale testing
The outcome: Making sure that the app is fast and reliable
Software performance testing is non-functional. It makes sure that the app is stable, responsive, and fast. This type of testing identifies errors that cause lagging or failures of the software. It finds bottlenecks and defines what is the heaviest data load that the system may handle. Testing data load can be also conducted separately with the help of load testing. It is carried out with such tools as JMeter, LoadRunner, or WebLoad.
The most recent marketing research conducted by Google claims that 53 percent of users are likely to leave a web page if it does not load in three seconds. If you do not want to lose users, performance testing is a must.
• Accessibility Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: Testing team, UI/UX designer, or BA
When conducted: Before the product is delivered
The outcome: Making sure that the app is accessible to everyone
The idea of accessibility testing is to make sure that the program can be used by the elderly and people with disabilities, such as vision impairments, hearing impairments, or mental disorders. The most basic software accessibility checklist is provided by the United States Department of Justice here.
In fact, an American company whose web page does not meet accessibility requirements can be subject to legal liability and a huge fine. Accessibility testing helps to ensure not only the best experience for all users but also the legal security of your business.
• Security Testing
Type: Non-functional
Who conducts: Testing team
When conducted: During full-scale testing
The outcome: Making sure that the app is secure
The aim of security testing, also known as vulnerability testing, is to identify potential loopholes, which wrongdoers can use to break the system. It tests the ability of the system to withstand cyberattacks and malicious software. Also, security testing checks the reliability of authorization and authentication processes.
In general, data safety is the number one global technological concern. If the private information of your users was leaked, destroyed, or stolen, you could face serious legal consequences.
That’s It?
Today we’ve discussed different types of software testing that form the ground for the high quality of a software product. However, the understanding of quality is not limited to the abovementioned. There are many other effective and interesting levels of testing that can be applied to your specific case. Keenethics specialists are skilled in each of these.
Localization testing, for instance, is used to check whether a product works well in a particular culture, location, or environment. Black box testing, or simply box testing approach, can be applied to get a fresh view of the product. Box testing technique should be executed by people with no understanding of the internal structure of software. They haven’t seen the code and know anything about the internal processes of software creation.
Have you heard about stress testing? Stress test for a software product is like a crush test for a car. It checks your software for stability. You can combine stress testing with volume testing. The latter is used to examine how your software will function under a huge volume of data.
But suppose that your product might have some bugs. Why don’t you use static testing at first? It’s a type of testing that allows you to check bugs without executing the code. It’s like checking the errors on the surface before diving deeper. When some bugs are detected and fixed, you can use sanity testing to make sure that your product works properly.
And what if you want to find the best configuration for your software? Configuration testing is the best idea in this case! You’ll test your products against different types of configurations to find the most relevant one. And when your product is ready for release, the most interesting happens. Your users can evaluate your product via usability testing.
As you see, the list of testing types seems to be endless. Risk-based testing, beta and scalability testing, component testing, compliance testing, penetration testing… Do you feel like your head’s boiling now? In fact, to ensure that your product is of high quality, you should not learn all these types by heart. The better decision is to trust your software to QA professionals. They will not only choose the most effective methods but also provide you with support and maintenance!
To Wrap Up
Different software testing methodologies are easier to understand than they seem. However, most of them are far from easy to conduct.
Yes, Quality Assurance takes time and requires some additional expenses and efforts. However, do not neglect it. Proper testing will help you avoid critical technical and business logic mistakes. To carry out the software testing process properly, keep record of the process according to the rules of QA documentation.
Finally, look for trusted QA specialists, who will work hand-in-hand with your development team. After all, testing your software is making sure that it is performant, reliable, and enjoyed by your users.
Let our professional QA team help you solve your software issues. Learn more about development and software testing services that we offer.