Do you want to learn more about Product Data Management? This article offers a full-scale guide to this topic.
I. Introduction
Current research clearly showcases what drives humankind towards progress and collapse. According to modern researchers, the key difference between primitive and advanced societies is their ability to establish and test hypotheses. In advanced societies, social and natural sciences employ increasingly complex methods. How will future societies outpace ours? Primarily through the increasing importance of science in society.
One of the key methods in this regard is data collection. For example, improved knowledge of chemical elements helps create better alloys. Similarly, manufacturing experts benefit from knowledge of multiple construction methods. The more data you have, the more options are present for product development. Even if other scientific methods don’t change, you’ll have additional information for review.
Consequently, we see two paths for improving your processes in modern manufacturing. On the one hand, you can improve your methods for reviewing data. Tools like AI will help perform better categorization through experiments and simulations.
On the other hand, you can try to collect more data. In this respect, the key technology involves various data management tools. This article, in particular, will deal with Product Data Management Software.
II. Defining Product Data Management (PDM)
Let’s start with the key concept in this analysis. This concept is Product Data Management (PDM).
A. Formal definition of PDM
What is PDM? Product Data Management stands for systems that help control internal product information. All companies have external or internal projects they work on. Many of them turn into full-scale products that go to the market. PDM apps exist to help record all information about them throughout the existing app lifecycle. Why is this so important? Changes in organizations are inevitable. Sometimes, entire teams working on some products disband. In this situation, losing vital documentation and tacit knowledge of a product is easy. As a result, fixing bugs in a developed system may become difficult or even impossible. PDM frameworks collect data on design and development files, documentation, and testing reports. In this way, these apps create a full-scale history of products that can be used for management goals later in their lifecycle.
B. PDM illustration
The best way to understand various definitions is to create analogies and examples. So, what’s a good example here? Imagine that your company creates tools for hospitals with the help of 3D printers. Why would you need to collect information on your product? Firstly, it may be useful for marketing. A strong product showcase will attract many people to your site. Secondly, some modifications to the initial product may be necessary later. If you fail to collect all CAD information, your firm can become unable to do this. New developers will either be incapable of understanding all the intricacies of a product or have no templates. Proper PDM will be able to help you avoid this problem.
High-quality PDM tools will have all the necessary information for your project. They’ll store several versions of a medical tool you were developing in the past and have all developer commentaries. In short, PDM is akin to an archive monitoring the progress of your project. If your customers need major modifications, you’ll be able to deliver them.
III. The Necessity of PDM in Today’s Market

PDMs are central to the modern markets. Let’s review why:
A. How product development has evolved
The first reason for the rise of PDMs is the evolution of product development in the modern world. In the past, projects were less complex than they’re today. The complexity of our society is steadily growing. In addition to complex engineering for hardware, we now have to create even more advanced software solutions. Programming alone isn’t overwhelmingly difficult. What makes various projects difficult is the need to create advanced programs for already advanced tools. In the 19th century, most factories needed machines. Now, most factories need a combination of machines and code. The mathematical complexity of modern industry is steadily growing. ITProToday reports many managers notice this factor and openly report it.
More importantly, complexity grows not only due to software aimed at manufacturing and production. We now create software to control software. Everything is becoming increasingly digital. In this light, product development is much harder than in the 19th or 20th centuries. The managers have to wrestle with multiple important process challenges:
1) Increasingly complexity of our machines (computers, for example);
2) Increasing complexity of our software;
3) Increasing complexity of interactions between software and hardware.
While a mere 50 years ago, most managers cared about hardware alone, they now have to understand software, too.
B. The increased complexity of product data, making PDM crucial
The increasing complexity of the relevant projects makes control difficult. This factor is reflected in the growing number of managers within modern developed economies. According to Data USA, the number of managers in the United States grows by approximately 3% yearly. Today, there’s one manager per 11 people in the American workforce. Most likely, this proportion will become smaller with time. More and more people are needed to control all project data in the US.
Why does this occur? In our opinion, the key reason for the rise of the managerial workforce is the increasing complexity of the US economy. Many projects are becoming more and more difficult to work with. A combination of software and hardware requires a more complex economy. In this light, it’s unsurprising that most companies start encountering problems with tracking project information. After all, our entire economy is more complex these days. Ultimately, there are two solutions to resolve this difficulty. One can hire more managers to collect as much data as possible. Another approach is to use advanced software for project management. In our opinion, this is the best solution to the issue we’ve outlined.
C. Role of PDM in ensuring competitiveness
PDM software is the best way to manage the outlined problem. Why? Such apps do two things that can’t be done via a human workforce. Above all, they engage every person in the data collection process. These systems automate various actions and minimize organizing efforts for the average worker. More importantly, they prevent situations in which you must rely too much on managers.
In a system that records all vital product data, transferring products to different teams is easier. Even if all your developers and managers leave some projects, restarting them should be simple. In this light, PDM increases your ability to manage products as you see fit.
Why is this so important for ensuring competitiveness? In our opinion, a potent PDM, above all, solves the issue of vendor lock-in. If you have full-scale data on your products, switching between teams should be easier. For instance, a PDM system enables you to start developing with one company and continue your journey with another. Besides, systems of this type make your development efforts more centralized. When you can review your entire product lifecycle, adding or remaking features in it is easier. Consequently, PDM meaning in modern IT and manufacturing is tremendous. This technology genuinely transforms your interaction with past and new products.
IV. Core Components of PDM
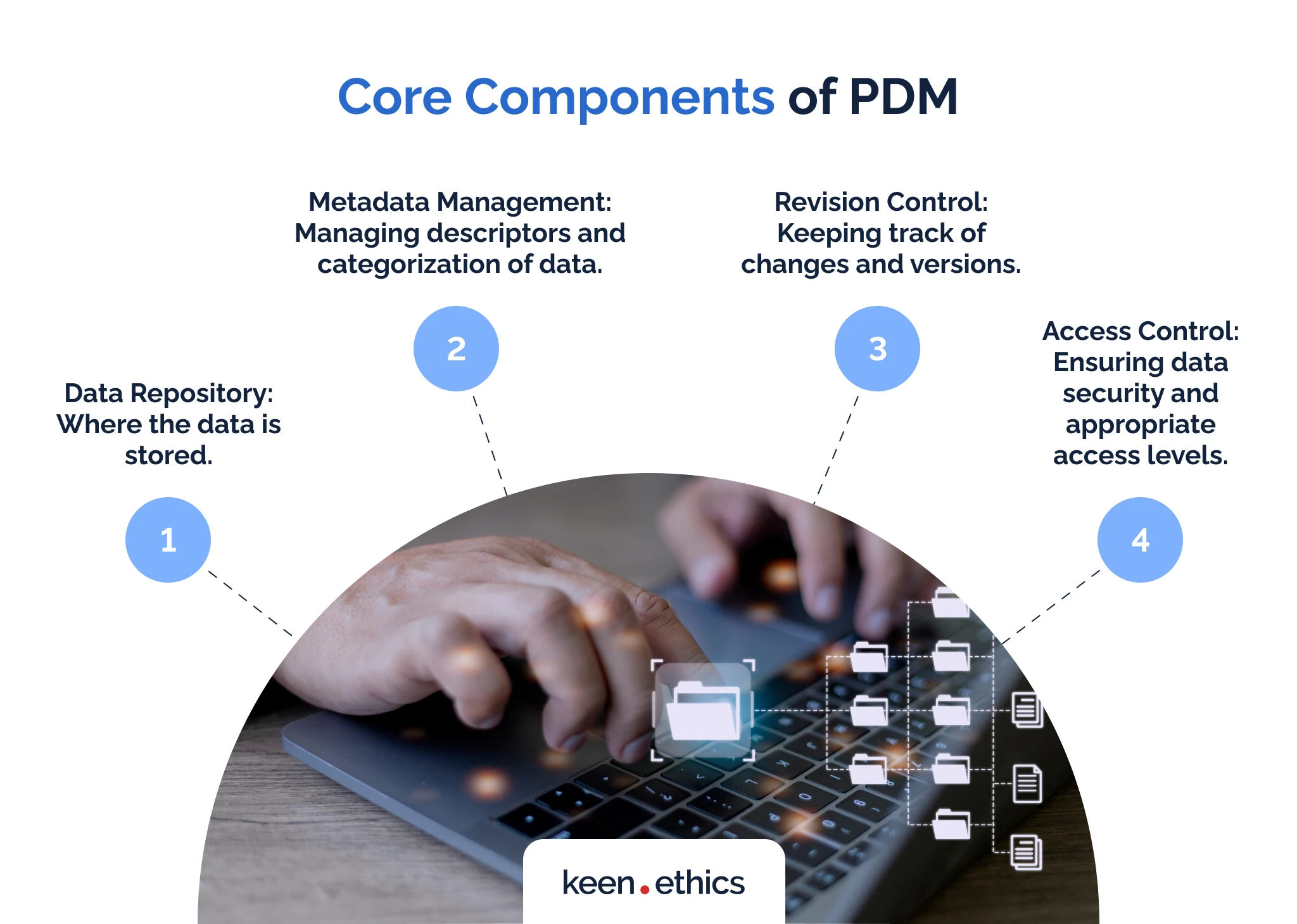
Every PDM has multiple components you need to pay attention to. Here are the key aspects you should consider:
A. Data repository: Where the data is stored
The primary aspect of an advanced PDM system is proper data storage. Every system of this type is primarily an information repository. Consequently, when choosing a PDM framework, you should understand how it stores data. In this regard, two options exist. Both have their downsides and positives. Let’s review these options in depth:
1) In-house data storage
In-house data storage is what it says on the tin. In this case, all the key project data is present only within a computer system of some organization. This approach has both positive aspects and major downsides. On the one hand, you don’t rely on outside organizations and fully control the data. This disposition prevents vendor lock-in and potentially boosts security. For example, setting up proper access control is easier in such systems.
On the other hand, these systems also create major barriers for workers. For instance, it may be possible to access data only from an office. In this system, hiring an outsourcer team is more difficult. When is this approach perfect for modern companies? In our opinion, it’s great when you need to focus on maximal confidentiality. In-house PDM frameworks are extremely secure because it’s possible to completely cut them off from the Internet.
2) Cloud storage
Investing in clouds is another significant option for a PDM or PLM (project lifecycle management) app. Clouds represent outside storage for your project. Usually, it occurs in a well-separated virtual space online. What are the benefits and negatives of those systems? In our opinion, they’re as numerous as in the case of in-house data storage.
On the one hand, cloud storage enables work from any place. More importantly, it removes ties to certain locations. You won’t lose your project data if a disaster happens in your area. Consequently, the probability of losing your data is generally lower in such systems. There’s also a smaller reliance on geographically bound teams.
On the other hand, those systems also have a major problem. They’re less reliable than internal servers from the standpoint of cybersecurity. Clouds are constantly online. As a result, outsiders can find a way in. If you host vital project data in the cloud, this can easily end in long-term negative outcomes for your business. After all, unscrupulous competitors may try to steal your project data. Some artifacts in PDM systems cost millions of dollars. This means data leaks are often unacceptable. Ultimately, we recommend cloud storage only for those projects that can withstand leaks.
B. Metadata Management: Managing descriptors and categorization of data
Choosing data storage format
A major element in any PDM framework is the data storage format. Every project has a significant amount of data associated with it. Some projects involve thousands of people. For example, large-scale animation often requires genuinely massive teams. In this light, you need to consider a correct standard for data categorization. Otherwise, data storage is useless. If its users can’t find the key information, there’s no point in creating such a system in the first place.
We believe product data management requires active metadata management. In this regard, a PDM framework must have strong tools for working with descriptors. What should it include?
Steps for metadata management
In our opinion, the following elements are essential:
1) Automatic assignment of metadata based on work context. Why is it so vital? In our opinion, such an approach helps find information even if the workers fail to name some work files properly. Problems such as typos occur often and easily lead to major data losses.
2) Tools for sorting data. Apart from metadata, you should also have frameworks categorizing the key information. For example, you must be able to sort data according to the creation date. The best systems have many options for sorting. One should be able to find information through tags or file titles.
3) Data search frameworks. Proper metadata should also give users an ability to search within various files. Most files have text-based content. Your system must be able to find this content. In our opinion, there’s even space for innovations. Modern AI systems can easily improve your ability to search for data. In this respect, we see two applications for this technology. On the one hand, a generative AI can help you find vital data. On the other hand, an image-centric AI may be perfect for searching visuals in some of your projects. The capabilities of modern AI are sufficient to enable such uses.
C. Revision Control: Keeping track of changes and versions

Revision control is a major feature in any PDM or PIM (Product Information Management) framework. It’s not enough to install a PDM system to track some files. In fact, this use case is easy to organize with other tools. A proper approach to categorizing system data can already be sufficient.
So, how do PDM frameworks distinguish themselves? Above all, they do this through their ability to control revisions. Revision control allows you to review data and track its changes. For example, a full-scale PDM lets you see all versions of an engineering project. In this way, you’ll be able to track daily progress in it.
Why are such features so important? We believe product data management software makes this feature vital for at least two reasons. The first reason is the ability to create better estimates for your projects and control productivity. A PDM allows one to see how much work people do every day. More importantly, it enables you to review how much time every task takes. With this data, it’s genuinely easier to understand how fast you can work with one project or another.
The second reason for enabling such systems is data preservation. Let’s imagine your product has a construction fault that ends in malfunctions occasionally. Finding this issue may be difficult in a complete project. You’ll have to take apart every component to understand what’s wrong. If you have access to older project versions, it’ll be easier to simulate problems. All you’ll need is to find the most probable areas of failure and search for a moment when an issue occurred for the first time. In short, a PDM can be essential for your development efforts.
D. Access Control: Ensuring data security and appropriate access levels.
A final element of a potent PDM design is proper access control. Most projects contain a lot of sensitive data. It may become especially sensitive if one can review it in development. As a result, you should have clear access limits. Only select people must be able to access certain aspects of your project. Various firms have newcomers in low-impact positions. Without enough control over them, the risk of data leaks is high. Only top managers should know the most vital information. The possibility of mixing data access levels has to be minimal.
Ultimately, we recommend going as far as to install zero trust systems. These frameworks give complete access only based on context. In this way, the possibility of massive data leaks decreases because even top users can use corporate systems only from certain locations. Obviously, putting data into a written form and then consigning it to a safe with a mechanical lock is even better. Still, zero trust access control typically gives us the greatest safety on the web.
V. Benefits of Effective PDM

PDM brings about multiple benefits for modern companies. Here are some of the key things you need to consider:
A. Efficiency in product development
Above all, a PDM can boost your efficiency in product development. How exactly? These are some positive outcomes such systems deliver:
- Improved ability to track productivity. It’s easier to discover slowdowns or improvements in the overall development process. PDMs create clear records for most product processes. Consequently, you’ll be able to understand how much time every artifact in your company requires.
- Improved ability to understand project evolution. The best way to understand some object is to see it in evolution. Humans started to realize what life is only with the advent of evolution theory. A PDM solution is notable for its ability to promote a similar effect. It allows the managers to see their projects in evolution. They can track all the principles of their development. In this way, finding problems in your project becomes easier, too. If you need major transformations for some systems, a PDM enables you to make them fast. Why? Because it helps you see what can go wrong in your system faster.
- Decreased bureaucracy. A major issue many projects face in modern IT is bureaucracy. Often, developers have to undergo several rounds of approvals to get data. With a PDM, this problem may finally go away. How exactly? Such systems offer high-quality tools for access control. As a result, you’ll be able to decide what employees can and can’t see once and for all. There’s no need to have separate meetings for multiple types of data access.
B. Reduction of errors and improved product quality
Here’s how PDM systems help reduce errors and improve product quality:
- PDM systems provide a single source of truth for product data. This information means there’s only one place to find the latest and most accurate information about a product. Why is this so important? Various errors occur due to inaccurate data. PDM frameworks genuinely help remove this inaccurate data. Different departments no longer have to guess what their colleagues want. Instead, they get the key information without any barriers.
- PDM systems help automate product data validation and approval processes. This approach assists with catching errors before they appear in production. A company without PDM risks leaving content without proper approval. Consequently, low-quality elements can become a basis for ECAD development.
- PDM systems provide better visibility into product data. This factor helps identify and correct errors more quickly. Multiple managers and rank-and-file employees can now review the key data. As a result, certain aspects of your project will be under improved control from several employees.
- PDM systems can help improve communication and collaboration between different departments. This approach prevents errors from happening in the first place.
Overall, PDM systems improve product quality by reducing errors, boosting data accuracy, and providing better visibility into product data. These benefits can lead to increased customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
C. Facilitating collaboration among cross-functional teams

As mentioned above, PDMs reduce errors by easing data sharing between departments. Another important thing they promote is full-scale cooperation between those groups. With a PDM, every department can easily spread information about its activities. This means that people from different departments will be able to understand how they fit into the overall hierarchy. Ultimately, this is essential for creating cross-functional teams. Diverging members of such teams wouldn’t have questions about other departments when they can share data on their actions. Consequently, they’ll be able to perform their work more efficiently.
What’s more, data sharing has become easier, too. Even when away from their departments, members of the cross-functional teams will be able to communicate changes to them properly.
D. Streamlined operations, leading to cost savings
Product Data Management (PDM) systems help businesses streamline operations in many ways. PDM tools can help organizations bring products to market faster by boosting efficiency, reducing errors, and improving communication. What’s more, they upgrade product quality and reduce development costs. Why does this occur? The key benefit of a strong PDM is information centralization. In one way or another, a PDM framework boosts your ability to manage products. Improved management, in turn, reduces slowdowns in the average product development. Many companies are prone to bureaucracy. In turn, PDM systems are extremely potent at removing those bureaucratic hurdles.
VI. Implementing PDM: Best Practices

If you’re reading this article, you most likely want to implement PDM. The key question to answer here is how to implement it. Let’s look at the best practices to consider in this regard:
A. Choosing the right PDM software/tool for your organization
Above all, you should learn how to choose the right PDM software and tools for your organization. Picking the right PDM software can be daunting, given the wide range of options available. Here are ten key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Understand your needs
- Identify your needs: clearly define your organization’s specific requirements for PDM software. You should consider factors such as product complexity and team collaboration needs.
- Evaluate features and functionality: assess the features and functions offered by different PDM software. Your goal is to ensure they align with your identified needs. Consider aspects like data management, revision control, and integration capabilities.
- Consider scalability: Choose PDM software to scale your organization’s growth. Some PDM tools are great for many small products. Others better accommodate big products with tremendous amounts of internal data. Your goal is to prepare for future increases in product complexity.
- Review ease of use and training: evaluate how user-friendly PDM software is and consider the training resources available. Some tools can have great features but are too difficult to implement. When choosing a PDM framework, you should consider smooth implementation and adoption. MCAD tools are often advanced enough to require big management teams. Don’t make management even more complex by choosing the wrong tools.
- Study your integration capabilities: Ensure your PDM software can integrate with other systems in your organization. It will be inefficient without ERP, CAD, and PLM tools.
Analyze existing capacities
- Analyze vendor reputation and support: Choose a PDM software vendor with a strong reputation. It should have positive reviews regarding reliability, customer support, and ongoing software development.
- Understand cost-effectiveness: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for your PDM app. What are some key aspects to consider here? Don’t think about the initial purchase prices alone. They’re only a part of what makes development costly. You should also look at maintenance fees, training costs, and potential customization expenses.
- Choose cloud-based vs. on-premises approach: Decide if a cloud-based or on-premises deployment of PDM software better suits your requirements and capabilities. What are those? You should look at infrastructure, security requirements, and IT expertise.
- Mind security and compliance: Ensure PDM software meets your organization’s security standards. It should also fulfill regulatory compliance requirements for data protection and privacy.
- Look for a proof of concept and pilot testing: consider conducting a proof of concept or pilot test with selected PDM software. This approach is essential for gaining hands-on experience. In our opinion, the best way to understand anything is through practice. Practice is what makes everything perfect.
B. Ensuring proper training and onboarding
We’ve already mentioned that training costs are a significant aspect of PDM installation. Proper implementation is impossible if you don’t pay attention to this factor. What should you do in this regard? In our opinion, the following steps are essential for a successful implementation of a PDM system in your business:
- Define training objectives: clearly outline your training program’s goals. This approach will help you tailor the training content. More importantly, you’ll be able to ensure it addresses the most critical aspects of PDM.
- Develop training materials: create comprehensive training materials covering all PDM system aspects. What should you include here? Consider features, functionalities, and best practices. Another important aspect is form variety. People learn through a combination of audio, visuals, and text. As a result, you should include user manuals, video tutorials, and interactive simulations.
- Identify training roles: assign roles and responsibilities to individuals involved in the training process. For example, you’ll at least need a lead training specialist and support staff.
- Conduct pilot training: conduct pilot training sessions with a small group of representative users for your testing material. Your goal is to identify any areas for improvement. In this way, full-scale training will be genuinely efficient.
- Deliver training sessions: roll out the training program to all users after testing. Your goal here is to provide both group sessions and individual hands-on training. Encourage active participation and address any questions or concerns raised by users.
- Provide ongoing support: establish mechanisms to assist users as they transition to the new PDM system. This may include a help desk, a knowledge base, and online forums.
- Evaluate training effectiveness: regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the training program by assessing user feedback and measuring training outcomes. This approach is the key way to identify the vital areas for improvement.
C. Regularly updating and maintaining the PDM system
A major step to consider while working with any type of PDM is regular updating and maintenance. What are the key steps to take here? Let’s review them:
- Constantly monitor version reports from your PDM developer. In this way, you’ll be able to spot if any critical bugs appear in the past systems.
- Review updates for the key libraries and platforms used in your PDM. Sometimes, major disrupting bugs can arise not in PDM software but in its basis. You should be on the lookout for such security crises. Otherwise, you risk encountering long-term negative consequences for your security.
- Install updates for your PDM software or its internal code immediately. Many updates feature some vital security upgrades. When bugs like Heartbleed appear, only full-scale updates can prevent them. If you fail to install them, you risk encountering long-term security issues in your company. A firm that doesn’t update its software is a perfect target for hackers.
- Monitor the feature requests of the users. You should review user requests if you’re working with custom PDM software or a proprietary one that enables extensions. Why? Often, users can highlight features that need major transformations. No amount of testing before deployment will replace long-term practice in real work. Consequently, active user feedback reviews can provide you with many interesting ideas.
- Update your app based on user requests. Upon analyzing user requests, you should update your PDM app to fit their needs. Advanced features like AI can save your designers a lot of time. You should always have a separate team for reviewing user requests and using them in development.
D. Establishing a data governance framework
Lastly, your key goal is to establish a full-scale data governance framework. What should you do here? In our opinion, the following actions are essential:
1. Identify data governance goals and objectives:
- Establish clear and measurable data governance goals aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Define the scope of data governance: understand the data types and processes you must govern.
- Determine the desired outcomes of data governance. Do you want improved data quality? Or is your goal to increase data accessibility? You should clearly understand what to do with your PDM system.
2. Identify and classify data assets:
- Create a comprehensive data inventory that identifies all data assets within the organization.
- Gather metadata about each data asset, including source, format, ownership, and sensitivity level.
- Classify data assets based on their importance and regulatory requirements.
3. Establish data governance policies and procedures:
- Develop clear and concise data governance policies that address your needs. For example, you should outline standards for saving files. Another important issue includes formats for storing MCAD data.
- Define data ownership roles and responsibilities to ensure data quality and security accountability. You should have a well-defined team of data security managers. Rank-and-file workers should also clearly understand their role in enforcing proper data standards.
- Implement data access controls to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
- Establish data quality standards to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency.
- Implement data retention and disposal policies to manage the lifecycle of data. Besides, you should understand what data needs deletion to guarantee compliance.
4. Implement data governance tools and technologies:
- Use data governance tools to automate data quality checks and lineage tracing.
- Adopt data discovery tools to identify and classify data assets across your organization.
- Leverage data protection tools to encrypt sensitive data and protect against unauthorized access.
5. Establish data governance training and communication programs:
- Provide comprehensive training to employees on data governance policies, procedures, and tools.
- Communicate data governance initiatives regularly to raise awareness and promote adoption.
- Encourage feedback from employees to continuously improve the data governance framework.
VII. Case Study: Successful PDM Implementation at Magna Powertrain GETRAG

Introduction
Magna Powertrain GETRAG is a leader in the development of powertrains for cars. The company has over 40,000 employees worldwide and operates in 24 countries. Magna Powertrain GETRAG’s products are used in a wide variety of vehicles. They’re useful for cars, trucks, SUVs, and motorcycles.
Magna Powertrain GETRAG began using a PDM system in the early 2000s. The company selected a commercial PDM system and began implementing it at that time. The implementation process was complex and took several years to complete. However, Magna Powertrain GETRAG was successful in implementing the PDM system. Ultimately, this system had a significant positive impact on the company’s business processes.
Challenges faced before implementation
Magna Powertrain faced numerous product data management challenges before implementing a PDM system. Above all, the company had a complex product portfolio. After all, it was developing products for multiple companies. Regrettably, for the business, its product data was stored in various systems. This made it difficult to find and access the information. As a result, the redevelopment efforts started to suffer in this company. Finding data on new frameworks for the firm was increasingly confusing. A major transformation in the processes became necessary to continue developing and manufacturing products.
In addition, Magna Powertrain was struggling to collaborate effectively between its different departments. Product data was not centralized and was not easily accessible to all employees. Consequently, a system of double confusion arose in the company. On the one hand, it was difficult to find project data due to different information systems. On the other hand, the departments themselves were not cooperative.
The process of PDM implementation
Magna Powertrain selected a commercial PDM system and began implementing it immediately. The implementation process was complex and took several years to complete. However, the relevant business was committed to making the implementation a success.
The first step in the implementation was to identify the company’s product data needs. Magna Powertrain worked with its PDM vendor to develop a customized PDM solution. Why? Only such a solution was capable of meeting the direct needs of this firm.
The next step was to migrate product data to the new PDM system. This was a complex task that required careful planning and coordination. It involved several vital steps for the presented company.
Firstly, it had to install its PDM solution on all digital devices. More importantly, it was crucial to ensure the maximal security of this solution. Any data leaks from its projects could have been devastating for the clients.
Secondly, a major aspect of success was to focus on transforming the existing practices in the business. Once the product data had been migrated, Magna Powertrain began training its employees on the new PDM system. The company also developed some processes to ensure the PDM system was applied well. Many departments were used to older practices. As a result, it was necessary to break the existing traditions in those departments and push them to access innovations. Doing this was extremely difficult due to the lack of department cooperation. An uphill battle to launch cooperation between various manufacturing departments started. Ultimately, the business managed to win in this regard, too. After several years of adaptation, the majority of the departments reached a similar wavelength. Consequently, the company has achieved an organized approach to data management.
Tangible outcomes and benefits post-implementation
The implementation of the PDM system had several tangible benefits for Magna Powertrain. These benefits include:
- Increased productivity;
- Improved product quality;
- Reduced time to market;
- Lower costs.
In addition, the PDM system has helped Magna Powertrain improve its department collaboration. This has led to a more efficient and effective product development process. Implementing a PDM system has been a full-scale success for Magna Powertrain.
Lessons learned
Several lessons can be learned from this case. These lessons include the following elements:
- It’s important to carefully plan and coordinate the implementation process.
- Developing a customized PDM solution that meets the company’s specific needs is critical.
- It’s essential to train employees on the new PDM system.
- Developing processes and procedures is indispensable to ensure that the PDM system is used effectively.
By following these lessons, other companies can increase their chances of success.
VIII. Common Misconceptions about PDM
Many myths surround modern PDM tools. Here are some of the key aspects you should consider:
A. Clearing up the confusion between PDM and similar systems, like PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)
Multiple systems with similar titles exist on the market. These are PLM and PIM frameworks. In these sections, we want to showcase how PDM tools are different from them:
- PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) tools manage the entire lifecycle of a product. This means such a system starts from ideation and design. Then, it transitions into manufacturing, sales, and support. PLM systems typically include a wide range of functionality. They help with product data management (PDM), product configuration management (PCM), and enterprise resource planning (ERP).
- PIM (Product Information Management) frameworks focus on managing product information. For example, it includes artifacts such as product descriptions, images, and specifications. PIM systems are typically used by marketing and sales teams. Why? Their key goal is to distribute product information to customers and partners.
- PDM (Product Data Management) is a subset of PLM that focuses on managing engineering data. What are some of those frameworks? They include CAD drawings, BOMs, and specifications. Engineers use PDM systems to manage the design and development of products.
B. Addressing myths about the complexity or cost of PDM
Common myths about Product Data Management (PDM) include misconceptions about complexity and cost. Contrary to belief, PDM solutions are designed to streamline data management. Many modern PDM systems offer user-friendly interfaces and intuitive workflows, reducing complexity. This means you’ll be able to spend less money on a project by cutting down work time. Additionally, the cost of PDM implementation can be outweighed by the long-term benefits of improved collaboration. For example, cloud-based PDM solutions allow people from multiple time zones to work on one project.
IX. Future Trends in PDM

Product data management solutions are evolving. Let’s look at the features you need to consider:
A. Integration of AI and machine learning in PDM
The most likely revolution in PDM will stem from AI and machine learning. How exactly can those technologies help? In our opinion, they’ll have multiple effects. Firstly, AI in PDM will automate many data storage tasks. For instance, AI and machine learning tools will be able to establish naming conventions and tags automatically based on content. They now have the ability to properly respond to text and images. You can use them for data categorization.
Secondly, a major impact will stem from the ability of PDM to analyze data and find errors in it. We believe that PDM software will become potent enough to spot irregularities in CAD information. Why is this so important? In our opinion, these capabilities will be essential for preventing various incidents. Many tools will become more reliable with such frameworks.
Lastly, AI and machine learning are crucial for predictive analytics. They can analyze worker productivity and make major judgments on it. With this data, it’ll be possible to make advanced judgments on the productivity of your workforce. All in all, modern PDM tools will greatly benefit from AI automation.
B. The increasing role of cloud-based PDM solutions
Another important aspect to consider is the increasing role of cloud-based PDM solutions. In the past, most PDM solutions were in-house-centric. Why does this aspect change so much today? In our opinion, two key reasons exist for this transformation. On the one hand, more and more firms are transitioning to flexible workplaces. They need to offer data access from multiple locations. Cloud solutions are more suited to this goal.
On the other hand, cloud solutions are becoming increasingly secure. Tommy Montgomery, a Director of Information Security at Quest Software, reports that cloud developers actively work on boosting security. In this light, it makes more sense to invest in the cloud. With proper configuration, it’s as safe as on-premises storage. Simultaneously, your workers get an opportunity to work from any location.
C. How IoT and Industry 4.0 might influence PDM’s evolution
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0 are transforming manufacturing processes. We expect this impact to extend to product data management (PDM). Here are some of the ways in which IoT and Industry 4.0 might influence PDM’s evolution:
- Increased real-time data collection and integration. IoT devices can generate a vast amount of real-time data about product usage. This data can be integrated into PDM systems. In this way, you’ll get valuable insights into product behavior. As a result, proactive maintenance and support will become possible.
- Enhanced product lifecycle management. IoT data can be used to track products throughout their lifecycle. You may start from design and manufacturing and continue to usage and disposal. This method can improve supply chain management and optimize product design. Your managers and developers will be able to detect defects early on.
- Closed-loop product development. IoT data helps improve products through a closed feedback loop. A closed feedback loop involves the ability to directly answer customer feedback. Consequently, you’ll be able to meet the evolving needs of customers.
- Predictive maintenance and asset management. IoT and Industry 4.0 Big Data is useful for predicting when equipment is likely to fail. This means you’ll get an opportunity for proactive maintenance and downtime prevention. This can boost overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and reduce maintenance expenses.
- Real-time product traceability. IoT data can be used to track products in real-time. In this way, you’ll understand their location and condition throughout the supply chain. This approach upgrades inventory management and reduces product losses. This feature works especially well by integrating Industry 4.0 features like Big Data.
- Personalized product experiences: IoT and Industry 4.0 data can create personalized product experiences. It’ll help tailor product recommendations based on Big Data. For example, you’ll be able to provide usage instructions via customer behavior.
X. Conclusion
All in all, PDM plays a tremendous role in modern product development. PDM systems save a lot of time by creating a unified storage for product data. With such systems, you no longer have to wait for access permissions. It’s easy to preconfigure them before any work. Implement PDMs today, and you’ll see a major difference in your manufacturing practices. If you want assistance with this goal, our firm can help. Keenethics has over eight years of experience developing solutions in edtech, fintech, and manufacturing. Don’t hesitate to address us!
Develop one with Keenethics to upgrade your processes.