Cybersecurity is essential for modern firms. In this article, you’ll learn why.
I. Introduction
In the first half of 2022, 2.8 billion cyberattacks occurred. As various experts showcase, this number is rising all the time. More and more hackers motivated by state espionage or personal gain are appearing. In this light, cybersecurity becomes a vital activity for fintech. What is cybersecurity? This term signifies measures aimed at preventing criminals from stealing user data or using software breaches for illegal profit. For finance, this aspect is meaningful today due to the rise of fintech.
What is fintech? It stands for a combination of modern IT technologies with banking. Yes, those technologies make banks more comfortable to use. Nonetheless, they also bring about a significant obstacle. Information technology tools are complex enough to always possess some potential loopholes.
Online banks and AI-based investment apps need strong cybersecurity measures. Why? Cybersecurity is essential to the success of fintech solutions, since it helps protect the financial data of independent customers and businesses.
II. Benefits of Cybersecurity in Fintech

Let’s review the benefits of cybersecurity in fintech. As you can see, they’re significant:
A. Improved customer experience
The first reason to invest in data protection is improved customer experience. In our opinion, this factor works in two ways: service- and psychology-oriented.
Improved service
Any data threat such as a breach is a major dent in the customer experience. If a person loses money because of a vulnerability in bank services, they can encounter catastrophic consequences. For example, they may be unable to pay for college, making expulsion a real possibility.
A data breach can also lead to leaks of sensitive information. In the case of public individuals, it can quickly end in career-ending reputation damage. Data about medication purchases may reveal a lot. Obviously, none of these outcomes offer any positive customer experience.
Better cybersecurity is essential as it reduces the chance that these events will occur. The reduction involves collective expertise. Some people will encounter breaches, but they’ll become less common in general.
Improved psychological well-being
If a person holds a significant sum in their account, the probability of it being stolen may create psychological discomfort. Cybersecurity is a crucial way to fight it. Two-factor authentication and encryption create a feeling of safety for tech-savvy individuals.
We also recommend giving client-centric configurations to boost security. For instance, you can enable your clients to use 2FA physical keys. Offering phone call confirmations for all transactions from actual employees is also a good idea. Voice recognition and fingerprint scans are potent tools, too. After all, some criminals now use SIM card swaps, stealing mobile phone numbers. If there’s no additional layer of security, a financial account becomes completely vulnerable.
Some of the features we’ve mentioned can be premium: what matters here is choice. An improved customer safety experience will eventually lead to a greater popularity of your service. Give people peace of mind, and they’ll recommend your bank to everyone.
B. Improved data protection

Another vital benefit stemming from cybersecurity is improved data protection. In our opinion, it benefits both the fintech organizations and an average customer:
Benefits for fintech organizations
Most fintech organizations are continuously trying to expand. They establish new deals or create new solutions. An inability to protect internal data can end in significant losses for them. Firstly, information about innovations may leak. As a result, competitors of an involved fintech business will match features in development. If they’re revolutionary, all this can genuinely undermine the company. This risk alone makes cybersecurity a critical task for any fintech organization.
Secondly, there’s always a significant risk of data breaches exposing partners. The majority of deals involve some form of NDAs (non-disclosure agreements). Data breaches can easily disrupt them.
Consequently, a fintech business that doesn’t protect itself will face lawsuits. This aspect touches upon both companies and regular clients. Equifax had to pay 425 million dollars in settlement to help the victims of its 2017 breach. In short, cybersecurity is essential for protecting the secrets of all stakeholders.
Benefits for the clients
While for fintech data breaches mean financial losses, they can become much more dangerous for its clients. A software breach can end in many adverse situations for the customers. Some of them may lose their funds. Others may become a target of criminals after they learn about their assets. A data leak can expose medical information and lead to later job termination for a client. Why is this so dangerous? In various at-will-employment states, proving that termination occurred due to a disability is difficult, according to legal firms. In short, data leaks are dangerous for clients. Improved data protection becomes a significant benefit since it reduces risk for stakeholders. If a fintech organization uses several security methods, data breaches will become minimal. In this light, occasional problems will be easier to resolve through direct compensation.
C. Reduced risk of fraud
Lastly, improved cybersecurity reduces the risk of fraud. This benefit also affects both banks and the average users.
Benefits for banks
Many criminals target banks to defraud them. The idea is to use breaches in their software for personal gain. The most common vector of attack involves loans. How do criminals get them? They use fake identities. In the modern world, it’s incredibly easy to fake one’s identity, and many people use this.
This challenge is so pressing that a separate type of fintech organization appeared to counter them. Microfinance businesses work with fraud in mind. Their entire business model revolves around easy-to-get loans. They set tremendous interest not because of greediness but to counter dishonest actions. In this model, honest clients pay money for the less honest ones.
What’s the issue here? Various fintech organizations outside this sector are vulnerable to the same problems, too. So, 70% of banking businesses say they lose at least 500 thousand dollars through fraud every year. Cybersecurity tools, such as artificial intelligence, improve fraud protection and reduce losses. If you promote a strong culture of compliance in your organization, risks will be minimal.
Benefits for clients
Fraud is especially dangerous for fintech clients. Many criminal organizations create elaborate schemes to defraud users. We explore them in the section below. In our opinion, fintech companies should become more proactive in this respect. Firstly, they must send emails and other messages about potential threats. Many corporate users don’t ignore this data.
Secondly, some regulations must appear for Internet transactions. For example, users should be able to make large transactions only on verified investment sites. Any other transactions should be authorized only after bank workers directly call these clients. This direct oversight will enable better control of various fraudulent schemes. A bank worker can dissuade clients from sending large sums to a potential cryptoscam. These features will decrease pressure on average users and complicate life for scammers. As a result, tragic situations in which people lose all their life savings will become less common.
III. Types of Fraud
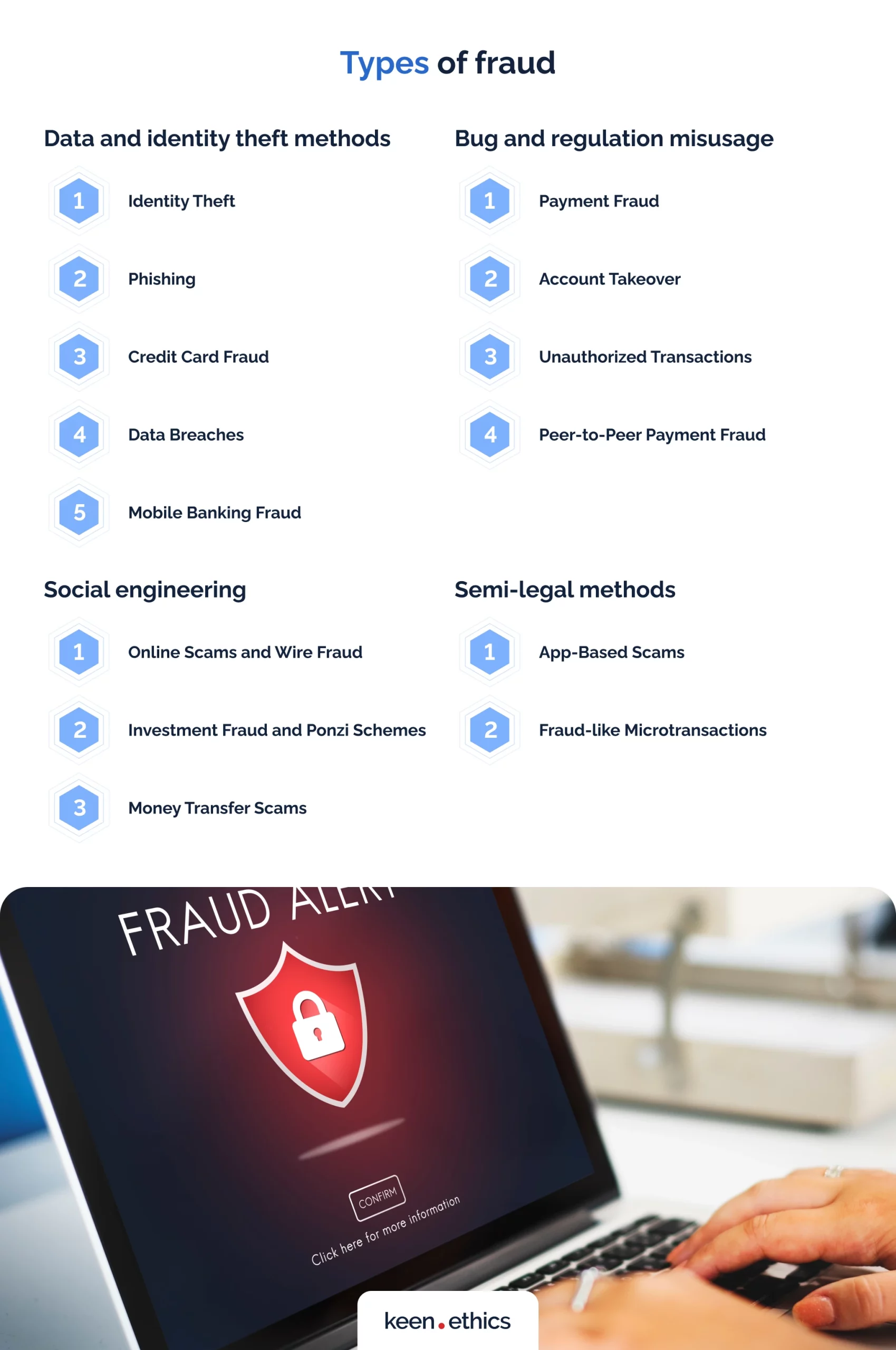
We believe it’s also essential for fintech users to know what fraud models exist on the market. As you’ll see, they’re numerous. Regrettably, some activities are even legitimate due to lack of regulation. Consequently, protecting yourself or your businesses against fraud is impossible without advanced knowledge of the topic. In this light, the users should be incredibly attentive to the following criminal acts:
A. Data and identity theft methods
- Identity Theft: criminals steal personal information to impersonate victims. They can then take out loans or even empty bank accounts with it.
- Phishing: criminals use messages that trick people into giving up financial or personal information. Common vectors of attack include emails and various messengers.
- Credit Card Fraud: criminals use stolen or counterfeit credit card data for unauthorized purchases.
- Data Breaches: in this case, criminals steal personal and financial data. Occasionally, it can involve sensitive information that is enough to bring down even the most secure systems.
- Mobile Banking Fraud: criminals exploit vulnerabilities in mobile banking apps to steal funds. One of the key ways to do this is the so-called SIM swap. The criminals use fake credentials to reissue your SIM. Through this vulnerability, they can later steal funds from your account.
B. Bug and regulation misusage
- Payment Fraud: this one includes deception in payment processing. The most common approaches involve practices like unauthorized transactions or fraudulent chargebacks.
- Account Takeover: hackers gain unauthorized access to financial accounts and manipulate them. This may happen through bugs in authorization systems or via SIM swaps.
- Unauthorized Transactions: this type of fraud involves unapproved financial transactions conducted without the account holder’s consent. Usually, they occur due to leaked credit card data. If the criminals know your credit card number and CVC, they can purchase anything online. A common approach is to invest stolen funds into the video game sector. Microtransactions and game codes are a perfect way to launder funds. The BBC reports that the situation is so adverse for many gaming businesses that they prefer piracy to code purchases. After all, they become the ultimate victims of fraud. When banks start returning stolen funds, they take them away from gaming companies.
- Peer-to-Peer Payment Fraud: Scammers misuse peer-to-peer payment services for illicit purposes. Once again, problems in their internal security are the most common way to steal funds. Phishing or even authorization bugs can act as a path to enter your account.
C. Social engineering

- Online Scams and Wire Fraud: these scams use social engineering to trick victims into giving up their information or money. They come in different forms. Modern fraudsters challenge themselves all the time to create new methods. For fintech users, standard methods include romance or work-from-home scams. As for businesses, the criminals can pose as superiors or partners. In short, the critical approach is to make victims trust the scammer enough to let the criminal access their funds.
- Investment Fraud and Ponzi Schemes: in this case, scammers provide fake or high-risk investment opportunities. In some cases, the idea is to steal money. A standard model is to set up fake trading sites with outrageous returns on investment. Various fake cryptoinvestment sites use this model. If users deposit small sums, they get some returns at first. Then, criminals trick them into larger investments. When these users deposit large sums there, they suddenly disappear. In other situations, the investments can be somewhat legit. What’s the catch? They’ll be high-risk, despite the claims of the criminals. In such schemes, fraudsters pay earlier investors with funds from newer ones. Ponzi schemes enrich early investors and devastate the later ones.
- Money Transfer Scams: multiple ways to use legitimate money transfers to scam also exist. What do criminals do? Scammers request money transfers, targeting vulnerable individuals. For example, a common scheme is to create fake fundraisers. Pity towards fake victims can push some people to send significant sums. The Federal Trade Commission (U.S.) also reports on family impostor scams. The criminals pose as family members to push their relatives to send funds. For instance, they can say they’re in a hospital and need emergency help.
D. Semi-legal methods
- App-Based Scams: some scammers create full-scale mobile apps to defraud users. These deceptive mobile apps trick users through various means. For example, they can steal credit card data. Another way to defraud clients is to add small fees for usage without informing them. For instance, an online game scam can take away money for every game session. What’s the catch here? This is the most challenging scam to defeat. Fraudsters tend to have legitimate terms of service and can hide behind them.
- Fraud-like Microtransactions: another challenge is that many legitimate companies use fraud-like approaches. Game Rant reports that large firms, such as Sega, never put limits on microtransactions in their mobile games. Situations where people link their credit cards to video games and spend all their funds are common. Children are especially vulnerable to this threat, spending exorbitant sums on their parents’ credit cards. This aspect doesn’t involve games alone. Fraudsters (and even ‘legitimate’ companies) can access credit cards to pocket user funds. A common ‘legitimate’ scheme is to prolong subscriptions without the user’s consent. In short, major regulation is crucial for this field.
IV. Challenges of Cybersecurity in Fintech

In our opinion, modern cybersecurity methods in the fintech industry face massive challenges. Here are some of them:
A. Complexity of security systems and their constant evolution
The first issue is the complexity of modern security systems. Scammers and hackers are continuously upgrading their methods. They do everything to maximize the efficiency of their illegal activities. In this light, we face two significant problems. Firstly, our security methods are already highly complex. We use mobile authentication, encryption, and AI to prevent fraud and data leaks. Those technologies require specialists with at least a Master’s degree to function well. Why? Most scammers are tech-savvy themselves. They know how modern security functions. As a result, we need specialists with outstanding profiles to guarantee safety.
Secondly, and more importantly, scams and hacks evolve all the time. A security system created two years ago is no longer valid today. It needs a constant flux of new features to guarantee a high level of security for its users. Scammers and hackers go down to lower and lower levels of computer software and hardware to succeed. Consequently, a security expert must know how computing works at all levels. Bugs such as Heartbleed require competence in both open-source and proprietary software. A security specialist must be able to read source code and even find viruses in the BIOS. Specialists must have universal skills to succeed.
Knowledge demands in this sector will grow further. In the upcoming 20 years, various experts will require Ph.D.-level expertise to succeed. This outcome will be especially probable if quantum computing technologies become mainstream. The experts will have to learn physics and understand how to use AI. In this light, the complexity of technologies will become high enough to make cybersecurity an arcane profession accessible only to elite specialists.
B. Cost of implementation

Obviously, the problems we’ve mentioned above lead to one important issue. The cost of implementing fintech cybersecurity will grow extremely fast. Perhaps, even exponentially. This growth in expenditures will come from two aspects. The education of a cybersecurity specialist will become more costly. More importantly, many solutions will require bigger teams of developers and security theorists. It’s also probable that more rank-and-file workers will be necessary, too. The role of fintech support specialists will become greater in the upcoming years. Atlantic IT company reports that up to 10% of IT business budgets go towards cybersecurity today. We expect this figure to grow in the future. Cybersecurity will combine three things that will make it pricier:
- Experts (theoreticians and developers) with at least a Master’s and preferably a Ph.D. degree;
- Expensive technologies such as quantum computing and AI;
- Various rank-and-file human experts who will monitor the most suspicious cases.
C. Lack of skilled professionals
Modern cybersecurity will require more specialists with advanced education. Does our education system produce enough of them? Jon Oltsik, a contributor at cybersecurity news website CSO online, claims that the answer is negative. We don’t have enough cybersecurity specialists even today.
What does this mean for the future of the fintech industry? In our opinion, the news is terrible: market demand for specialists is only growing. At some point, it may start losing the war against scammers and hackers. Only the wealthiest firms will be able to attract enough skilled specialists due to expertise shortages.
For this reason, it’s crucial to act now rather than in 10 or 20 years. What can you do? Primarily, a strong idea is to hire companies with advanced cybersecurity knowledge. More importantly, a significant path toward success is creating homegrown specialists. You should invest in your cybersecurity experts as much as possible. Offer them access to online courses on the topic and even, if possible, cover their investments in the Master’s and Ph.D. education. Bigger corporations should even go as far as to fund unique cybersecurity courses. In short, the time to act and create new specialists is now.
V. Strategies for Enhancing Cybersecurity in Fintech

Let’s review how one can boost cybersecurity in modern fintech:
A. Education and training
We’ve already mentioned that many fintech cybersecurity risks stem from the lack of expertise. In our opinion, this issue is two-fold. You should consider both specialists and rank-and-file workers.
Cybersecurity theoreticians and developers
Education is lacking among cybersecurity theoreticians and developers. We need more and more Ph.D. specialists in this field today. The best way to solve this problem is to transform government policy. We require more universities targeting this issue.
Another solution is to invest in expert education independently. Invest in Ph.D. degrees in your team, and you’ll see massive results. A vital path for securing your fintech firm against future threats is to expand the theoretical expertise of the employees.
You should also search for firms employing former and ethical hackers. These people usually have the greatest understanding of modern cybersecurity. If you invest in their improved education, they can serve a vital role in your organization.
Rank-and-file workers
Another group that benefits from significant investments in cybersecurity education and training includes rank-and-file workers. In this regard, every person in your firm should receive active training. What are some practices you can promote in the process?
Firstly, a strong idea is to teach your workers how to keep personal and work information safe. Practices like password reuse or sticky notes/text files with them should be prohibited by internal regulation.
Secondly, a positive standard is to regularly teach various workers about new threats. Both low- and middle-tier managers and their subordinates should know about modern cryptoscams and relevant Ponzi Schemes. This knowledge can easily save their customers from massive losses. Consequently, cybersecurity seminars should become a standard for fintech. The field evolves, so the workers must evolve together with it. One of the critical tasks for your cybersecurity theoreticians is to create information bulletins about the key threats. Even a one-week delay regarding some threat can be damaging.
B. Security audits

Another strategy for ensuring cybersecurity is to invest in security audits. This service is costly, but it can reveal pressing issues in your defenses. Here are the processes that an average security audit involves:
- Policy and Procedure Review: you look at policies and procedures to ensure they match the best practices and compliance requirements. Problems with password storage or non-disclosure can quickly be revealed at this stage.
- Access Control Assessment: examine user permissions and controls to prevent unauthorized access. Often, many companies allow low-tier employees to access data they shouldn’t have. Regrettably, this is a perfect entry point for hackers.
- Code vulnerability assessment: most fintech organizations rely on advanced applications. Any errors in their code can lead to massive breaches. In this light, it makes sense to perform full-scale code audits. Yes, they’re incredibly costly, but this practice guarantees long-term security.
- Incident Response Plan Analysis: sometimes, incidents are unavoidable. You should review your incident response plan to ensure it’s well-defined and up-to-date. Some breaches are inevitable; the key challenge is not to panic if they happen.
- Data Encryption Review: modern encryption tools are vital, but they require advanced expertise. You should verify that sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Moreover, it’s crucial to review the encryption tools themselves. Bugs such as Heartbleed exploit in SSL algorithms are, regrettably, common. Consequently, you should always be alert concerning potential problems.
- Network Security Examination: assess the effectiveness of firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems. There are no perfect apps on this market. Moreover, even one incorrect setting can make them completely inefficient. Remember: no testing is excessive.
- User Training Evaluation: if you have cybersecurity training, your chances of avoiding financial losses are high. Still, it’s not enough to have training per se. It should also be efficient. Your goal at this stage is to determine if employees receive adequate training. A low-quality cybersecurity course can, regrettably, create a false sense of safety.
- Physical Security Inspection: some hackers are bold enough to attack the headquarters of fintech firms. We know of cases when criminals posed as employees to target vital infrastructure. With such access, it would only take one infected USB stick to expose a whole fintech organization. What should you do at this stage? Inspect physical security controls, which include access badges and surveillance. Even a small access card can easily save your company.
- Third-Party Vendor Assessment: most firms use equipment and software from multiple vendors. You should evaluate their cybersecurity data before enabling those products in your networks.
- Compliance Verification: the best way to understand if you’re doing enough is to look at industry and government standards. At this stage, you should ensure your organization complies with them. Are they sufficient in all cases? No. Still, such standards usually represent the bare minimum you should target. They’re a sanity check for your organization.
C. Use of encryption
Occasionally, some criminals will get access to company data. Unknown bugs and vulnerabilities are unavoidable. However, if you encrypt everything correctly, even advanced access rights won’t give any vital data. Here are some fundamental standards that will help you encrypt passwords and user data:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
- DES (Data Encryption Standard)
- TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy)
A good idea is to also use tokens of various kinds. What’s the rule of thumb in this case? The more encryption, the better. There’s no such thing as excessive encryption. In fact, fintech organizations should go as far as to consider potential future technologies. Future-proofing is especially important for fintech because it deals with extremely sensitive data. In this light, we also recommend looking at quantum-proof encryption. Quantum computers can process data 100 trillion times faster than modern ones. If your encryption protocol withstands such power, it can withstand anything.
D. Use of AI
As we’ve mentioned before, the number of hackers and hacking threats is growing. This means more and more people will have to deal with this issue in the future. At some point, human resource demands may become excessive. What’s a solution? In our opinion, you should pay attention to AI. Modern algorithms can learn by using terabytes upon terabytes of data to make robust predictions. In this regard, we expect two types of technologies to rise. Firstly, Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT, will become cybersecurity consultants. They can inform users about the new threats in fintech. Secondly, we expect predictive models will use algorithms to find suspicious activity. These technological advances will let human workers focus on the most complicated cases. In turn, various tasks in cybersecurity will be automated.
E. Access Control
Many problems in modern cybersecurity stem from low-quality practices in access control. For example, some fintech organizations give too many access rights to rank-and-file workers. In this situation, a hacker can target lower segments of a work-related app and do a lot of damage. What should you do here? In our opinion, you should delineate access rights according to risk. The most vulnerable data should be accessible only to the top managers.
Ultimately, we recommend zero-trust frameworks. Even top management should receive access to fintech management tools only from specific devices and at a certain time. In this way, breaches will become minimal. Even if they occur, mitigating damage will be easy.
F. Incident Response Plans
Lastly, you should remember one sad truth about cybersecurity: breaches are inevitable. What’s your key development target in this light? Consider high-quality incident response plans. You should have a clear plan for dealing with breaches. In numerous instances, they can be genuinely company-saving. Why? Various hacks typically involve only a small area of your security system. If you cover it, further problems will be impossible. Ultimately, IBM reports that a good incident response plan decreases breach costs by 35%.
VI. Conclusion

To summarize, the importance of cybersecurity in fintech is tremendous. Modern fintech organizations lose millions of dollars yearly due to security breaches and fraud. In this respect, investments in cybersecurity are the best choice. Modern tools can’t remove all risks, but they minimize them. Invest in AI, access control, and encryption: they genuinely save costs. The more you invest today, the less you’ll have to pay tomorrow.
Develop your next cybersecurity solution for fintech with Keenethics!